
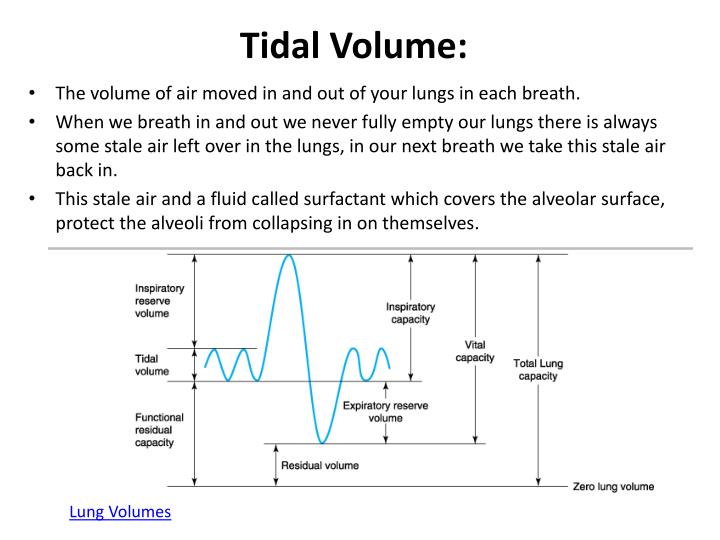
Ucdenver.edu nih predicted body weight tidal volume chart trial#
Trial planning may be better estimated by simulation than routine, simplistic calculations, but such simulations require detailed data of initial parameters. The PETAL Network considered performing a pragmatic stepped-wedge, cluster-randomized, controlled, hybrid implementation trial to examine systematic implementation of a default 6 ml/kg PBW LTVV strategy in patients with acute respiratory failure requiring intubation to improve adherence to LTVV and decrease mortality in acute respiratory failure. Consequently, there has been increasing call to apply LTVV for all patients with acute respiratory failure upon initiation of mechanical ventilation. LTVV may also benefit patients without ARDS. As a result, low–tidal volume ventilation (LTVV) is now recommended for all patients with ARDS, although penetration of this evidence-based practice has been limited, especially early in mechanical ventilation. BackgroundĪ previous study demonstrated improved survival among patients with ARDS receiving tidal volume (Vt) targeted to 6 ml/kg of predicted body weight (PBW). The two main goals of PETAL-LOTUS FRUIT were to conduct a prospective, observational study within all PETAL Network sites to determine the frequency of and outcomes from acute respiratory failure and the current usual care for tidal volume ventilation in patients with and without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and to simulate the design and power of the proposed LOTUS trial.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
